How a N-channel JFET Works

This article explains the operation of a N-channel Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET) and how to turn it on and how to turn it off.
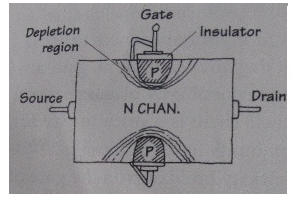
This is a typical diagram you would see of voltage biasing of a N-channel JFET. This diagram also serves
to show you all the parts of a N-channel JFET.
How to Turn on a N-Channel JFET
To turn on a N-channel JFET, apply a positive voltage (VDD) to the drain of the transistor with respect to the source (the drain must be sufficiently more positive than the source). This will allow a current to flow through the drain-source channel. If the gate voltage, VGG, is 0V, the drain current is at its largest value for safe operation, and the JFET is in the On condition.
So with a sufficient positive voltage, VDD, and no voltage (0V) applied to the base, the N-channel JFET is in maximum operation and has the largest current.
How to Turn Off a N-Channel JFET
To turn off the N-channel JFET, there are 2 steps you can take. You can either cut off the bias positive
voltage, VDD, that powers the drain. Or you can apply a negative voltage to the gate. This means you switch
the polarity of the voltage going to the gate. Instead of positive voltage, you apply negative voltage. When a negative
voltage is applied to the gate, the drain current is reduced. As the gate voltage, VGG, becomes more negative, the current
lessens until cutoff, which is when then JFET is in the Off condition.